This connection resiliency and command interception tutorial is optional. If you skip this tutorial, a few minor adjustments will have to be made in subsequent tutorials.
The original tutorial series, produced by Tom Dykstra and Rick Anderson ( @RickAndMSFT ) was written using the C# language. My versions keep as close to the originals as possible, changing only the coding language. The narrative text is largely unchanged from the original and is used with permission from Microsoft.
This tutorial series teaches you how to create ASP.NET MVC 5 applications using the Entity Framework 6 and Visual Studio 2013 Express for Web. This series uses the Code First workflow. For information about how to choose between Code First, Database First, and Model First, see Entity Framework Development Workflows.
The tutorial series comprises 12 sections in total. They are intended to be followed sequentially as each section builds on the knowledge imparted in the previous sections. Progress through the sections is reflected in a Visual Studio Express for Web project download that accompanies each section which features the web application that you build through the series.
Download the code
The code for this section is available here. Save the .zip file to a convenient location and then extract the contents. Make sure you have an edition of Visual Studio 2013 installed (Express for Web, Professional, Premium or Ultimate) and double click the .sln file. Once the project is opened in your IDE, press Shift+Ctrl+B to build the solution. This will ensure that all packages are restored from Nuget and may take a while depending on your Internet connection speed.
The navigation path through the series is as follows:
- Creating an Entity Framework Data Model
- Implementing Basic CRUD Functionality
- Sorting, Filtering and Paging
- Connection Resiliency and Command Interception
- Code First Migrations and Deployment
- Creating a More Complex Data Model
- Reading Related Data
- Updating Related Data
- Async and Stored Procedures
- Handling Concurrency
- Implementing-Inheritance
- Advanced Entity Framework Scenarios
Enable connection resiliency
So far the application has been running locally in IIS Express on your development computer. To make a real application available for other people to use over the Internet, you have to deploy it to a web hosting provider, and you have to deploy the database to a database server.
If you deploy the application to Windows Azure, you'll deploy the database to Windows Azure SQL Database, a cloud database service. Transient connection errors are typically more frequent when you connect to a cloud database service than when your web server and your database server are directly connected together in the same data center. Even if a cloud web server and a cloud database service are hosted in the same data center, there are more network connections between them that can have problems, such as load balancers.
Also a cloud service is typically shared by other users, which means its responsiveness can be affected by them. And your access to the database might be subject to throttling. Throttling means the database service throws exceptions when you try to access it more frequently than is allowed in your Service Level Agreement (SLA).
Many or most connection problems when you're accessing a cloud service are transient, that is, they resolve themselves in a short period of time. So when you try a database operation and get a type of error that is typically transient, you could try the operation again after a short wait, and the operation might be successful. You can provide a much better experience for your users if you handle transient errors by automatically trying again, making most of them invisible to the customer. The connection resiliency feature in Entity Framework 6 automates that process of retrying failed SQL queries.
The connection resiliency feature must be configured appropriately for a particular database service:
- It has to know which exceptions are likely to be transient. You want to retry errors caused by a temporary loss in network connectivity, not errors caused by program bugs, for example.
- It has to wait an appropriate amount of time between retries of a failed operation. You can wait longer between retries for a batch process than you can for an online web page where a user is waiting for a response.
- It has to retry an appropriate number of times before it gives up. You might want to retry more times in a batch process that you would in an online application.
You can configure these settings manually for any database environment supported by an Entity Framework provider, but default values that typically work well for an online application that uses Windows Azure SQL Database have already been configured for you, and those are the settings you'll implement for the Contoso University application.
All you have to do to enable connection resiliency is create a class in your assembly that derives from the DbConfiguration class, and in that class set the SQL Database execution strategy, which in EF is another term forretry policy.
-
In the DAL folder, add a class file named SchoolConfiguration.vb.
-
Replace the template code with the following code:
Imports System.Data.Entity Imports System.Data.Entity.SqlServer Namespace DAL Public Class SchoolConfiguration Inherits DbConfiguration Public Sub New() SetExecutionStrategy("System.Data.SqlClient", Function() New SqlAzureExecutionStrategy()) End Sub End Class End Namespace
The Entity Framework automatically runs the code it finds in a class that derives from DbConfiguration. You can use the DbConfiguration class to do configuration tasks in code that you would otherwise do in the Web.config file. For more information, see Entity Framework Code-Based Configuration.
-
In StudentController.vb, add an Imports statement for System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.
Imports System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure
-
Change all of the Catch blocks that catch DataException exceptions so that they catch RetryLimitExceededException exceptions instead. For example:
Catch Dex As RetryLimitExceededException 'Log the error (uncomment dex variable name and add a line here to write a log. ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists see your system administrator.") End Try
You were using DataException to try to identify errors that might be transient in order to give a friendly "try again" message. But now that you've turned on a retry policy, the only errors likely to be transient will already have been tried and failed several times and the actual exception returned will be wrapped in the RetryLimitExceededException exception.
For more information, see Entity Framework Connection Resiliency / Retry Logic.
Enable Command Interception
Now that you've turned on a retry policy, how do you test to verify that it is working as expected? It's not so easy to force a transient error to happen, especially when you're running locally, and it would be especially difficult to integrate actual transient errors into an automated unit test. To test the connection resiliency feature, you need a way to intercept queries that Entity Framework sends to SQL Server and replace the SQL Server response with an exception type that is typically transient.
You can also use query interception in order to implement a best practice for cloud applications: log the latency and success or failure of all calls to external services such as database services. EF6 provides a dedicated logging API that can make it easier to do logging, but in this section of the tutorial you'll learn how to use the Entity Framework's interception feature directly, both for logging and for simulating transient errors.
Create a logging interface and class
A best practice for logging is to do it by using an interface rather than hard-coding calls to System.Diagnostics.Trace or a logging class. That makes it easier to change your logging mechanism later if you ever need to do that. So in this section you'll create the logging interface and a class to implement it.
-
Create a folder in the project and name it Logging.
-
In the Logging folder, create a class file named ILogger.vb, and replace the template code with the following code:
Namespace Logging Public Interface ILogger Sub Information(message As String) Sub Information(fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Sub Information(exception As Exception, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Sub Warning(message As String) Sub Warning(fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Sub Warning(exception As Exception, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Sub Err(message As String) Sub Err(fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Sub Err(exception As Exception, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Sub TraceApi(componentName As String, method As String, timespan As TimeSpan) Sub TraceApi(componentName As String, method As String, timespan As TimeSpan, properties As String) Sub TraceApi(componentName As String, method As String, timespan As TimeSpan, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) End Interface End Namespace
The interface provides three tracing levels to indicate the relative importance of logs, and one designed to provide latency information for external service calls such as database queries. The logging methods have overloads that let you pass in an exception. This is so that exception information including stack trace and inner exceptions is reliably logged by the class that implements the interface, instead of relying on that being done in each logging method call throughout the application.
The TraceApi methods enable you to track the latency of each call to an external service such as SQL Database.
-
In the Logging folder, create a class file named Logger.vb, and replace the template code with the following code:
Imports System.Diagnostics Imports System.Text Namespace Logging Public Class Logger Implements ILogger Public Sub Information(message As String) Implements ILogger.Information Trace.TraceInformation(message) End Sub Public Sub Information(fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.Information Trace.TraceInformation(fmt, vars) End Sub Public Sub Information(exception As Exception, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.Information Trace.TraceInformation(FormatExceptionMessage(exception, fmt, vars)) End Sub Public Sub Warning(message As String) Implements ILogger.Warning Trace.TraceWarning(message) End Sub Public Sub Warning(fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.Warning Trace.TraceWarning(fmt, vars) End Sub Public Sub Warning(exception As Exception, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.Warning Trace.TraceWarning(FormatExceptionMessage(exception, fmt, vars)) End Sub Public Sub Err(message As String) Implements ILogger.Err Trace.TraceError(message) End Sub Public Sub Err(fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.Err Trace.TraceError(fmt, vars) End Sub Public Sub Err(exception As Exception, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.Err Trace.TraceError(FormatExceptionMessage(exception, fmt, vars)) End Sub Public Sub TraceApi(componentName As String, method As String, timespan As TimeSpan) Implements ILogger.TraceApi TraceApi(componentName, method, timespan, "") End Sub Public Sub TraceApi(componentName As String, method As String, timespan As TimeSpan, fmt As String, ParamArray vars As Object()) Implements ILogger.TraceApi TraceApi(componentName, method, timespan, String.Format(fmt, vars)) End Sub Public Sub TraceApi(componentName As String, method As String, timespan As TimeSpan, properties As String) Implements ILogger.TraceApi Dim message As String = [String].Concat("Component:", componentName, ";Method:", method, ";Timespan:", timespan.ToString(), _ ";Properties:", properties) Trace.TraceInformation(message) End Sub Private Shared Function FormatExceptionMessage(exception As Exception, fmt As String, vars As Object()) As String ' Simple exception formatting: for a more comprehensive version see ' http://code.msdn.microsoft.com/windowsazure/Fix-It-app-for-Building-cdd80df4 Dim sb = New StringBuilder() sb.Append(String.Format(fmt, vars)) sb.Append(" Exception: ") sb.Append(exception.ToString()) Return sb.ToString() End Function End Class End Namespace
The implementation uses System.Diagnostics to do the tracing. This is a built-in feature of .NET which makes it easy to generate and use tracing information. There are many "listeners" you can use with System.Diagnostics tracing, to write logs to files, for example, or to write them to blob storage in Windows Azure. See some of the options, and links to other resources for more information, in Troubleshooting Windows Azure Web Sites in Visual Studio. For this tutorial you'll only look at logs in the Visual Studio Output window.
In a production application you might want to consider tracing packages other than System.Diagnostics, and the ILogger interface makes it relatively easy to switch to a different tracing mechanism if you decide to do that.
Create interceptor classes
Next you'll create the classes that the Entity Framework will call into every time it is going to send a query to the database, one to simulate transient errors and one to do logging. These interceptor classes must derive from the DbCommandInterceptor class. In them you write method overrides that are automatically called when query is about to be executed. In these methods you can examine or log the query that is being sent to the database, and you can change the query before it's sent to the database or return something to Entity Framework yourself without even passing the query to the database.
-
To create the interceptor class that will log every SQL query that is sent to the database, create a class file named SchoolInterceptorLogging.vb in the DAL folder, and replace the template code with the following code:
Imports System.Data.Common Imports System.Data.Entity Imports System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception Imports System.Data.Entity.SqlServer Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.Diagnostics Imports System.Reflection Imports System.Linq Imports ContosoUniversity.Logging Namespace DAL Public Class SchoolInterceptorLogging Inherits DbCommandInterceptor Private _logger As ILogger = New Logger() Private ReadOnly _stopwatch As New Stopwatch() Public Overrides Sub ScalarExecuting(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of Object)) MyBase.ScalarExecuting(command, interceptionContext) _stopwatch.Restart() End Sub Public Overrides Sub ScalarExecuted(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of Object)) _stopwatch.[Stop]() If interceptionContext.Exception IsNot Nothing Then _logger.Err(interceptionContext.Exception, "Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText) Else _logger.TraceApi("SQL Database", "SchoolInterceptor.ScalarExecuted", _stopwatch.Elapsed, "Command: {0}: ", command.CommandText) End If MyBase.ScalarExecuted(command, interceptionContext) End Sub Public Overrides Sub NonQueryExecuting(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of Integer)) MyBase.NonQueryExecuting(command, interceptionContext) _stopwatch.Restart() End Sub Public Overrides Sub NonQueryExecuted(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of Integer)) _stopwatch.[Stop]() If interceptionContext.Exception IsNot Nothing Then _logger.Err(interceptionContext.Exception, "Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText) Else _logger.TraceApi("SQL Database", "SchoolInterceptor.NonQueryExecuted", _stopwatch.Elapsed, "Command: {0}: ", command.CommandText) End If MyBase.NonQueryExecuted(command, interceptionContext) End Sub Public Overrides Sub ReaderExecuting(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of DbDataReader)) MyBase.ReaderExecuting(command, interceptionContext) _stopwatch.Restart() End Sub Public Overrides Sub ReaderExecuted(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of DbDataReader)) _stopwatch.[Stop]() If interceptionContext.Exception IsNot Nothing Then _logger.Err(interceptionContext.Exception, "Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText) Else _logger.TraceApi("SQL Database", "SchoolInterceptor.ReaderExecuted", _stopwatch.Elapsed, "Command: {0}: ", command.CommandText) End If MyBase.ReaderExecuted(command, interceptionContext) End Sub End Class End Namespace
For successful queries or commands, this code writes an Information log with latency information. For exceptions, it creates an Error log.
-
To create the interceptor class that will generate dummy transient errors when you enter "Throw" in the Search box, create a class file named SchoolInterceptorTransientErrors.vb in the DAL folder, and replace the template code with the following code:
Imports System.Data.Common Imports System.Data.Entity Imports System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception Imports System.Data.Entity.SqlServer Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.Diagnostics Imports System.Reflection Imports System.Linq Imports ContosoUniversity.Logging Namespace DAL Public Class SchoolInterceptorTransientErrors Inherits DbCommandInterceptor Private _counter As Integer = 0 Private _logger As ILogger = New Logger() Public Overrides Sub ReaderExecuting(command As DbCommand, interceptionContext As DbCommandInterceptionContext(Of DbDataReader)) Dim throwTransientErrors As Boolean = False If command.Parameters.Count > 0 AndAlso command.Parameters(0).Value.ToString() = "Throw" Then throwTransientErrors = True command.Parameters(0).Value = "an" command.Parameters(1).Value = "an" End If If throwTransientErrors AndAlso _counter < 4 Then _logger.Information("Returning transient error for command: {0}", command.CommandText) _counter += 1 interceptionContext.Exception = CreateDummySqlException() End If End Sub Private Function CreateDummySqlException() As SqlException ' The instance of SQL Server you attempted to connect to does not support encryption Dim sqlErrorNumber = 20 Dim sqlErrorCtor = GetType(SqlError).GetConstructors(BindingFlags.Instance Or BindingFlags.NonPublic).Where(Function(c) c.GetParameters().Count() = 7).[Single]() Dim sqlError = sqlErrorCtor.Invoke(New Object() {sqlErrorNumber, CByte(0), CByte(0), "", "", "", 1}) Dim errorCollection = Activator.CreateInstance(GetType(SqlErrorCollection), True) Dim addMethod = GetType(SqlErrorCollection).GetMethod("Add", BindingFlags.Instance Or BindingFlags.NonPublic) addMethod.Invoke(errorCollection, New Object() {sqlError}) Dim sqlExceptionCtor = GetType(SqlException).GetConstructors(BindingFlags.Instance Or BindingFlags.NonPublic).Where(Function(c) c.GetParameters().Count() = 4).[Single]() Dim sqlException = DirectCast(sqlExceptionCtor.Invoke(New Object() {"Dummy", errorCollection, Nothing, Guid.NewGuid()}), SqlException) Return sqlException End Function End Class End Namespace
This code only overrides the ReaderExecuting method, which is called for queries that can return multiple rows of data. If you wanted to check connection resiliency for other types of queries, you could also override the NonQueryExecuting and ScalarExecuting methods, as the logging interceptor does.
When you run the Student page and enter "Throw" as the search string, this code creates a dummy SQL Database exception for error number 20, a type known to be typically transient. Other error numbers currently recognized as transient are 64, 233, 10053, 10054, 10060, 10928, 10929, 40197, 40501, abd 40613, but these are subject to change in new versions of SQL Database.
The code returns the exception to Entity Framework instead of running the query and passing back query results. The transient exception is returned four times, and then the code reverts to the normal procedure of passing the query to the database.
Because everything is logged, you'll be able to see that Entity Framework tries to execute the query four times before finally succeeding, and the only difference in the application is that it takes longer to render a page with query results.
The number of times the Entity Framework will retry is configurable; the code specifies four times because that's the default value for the SQL Database execution policy. If you change the execution policy, you'd also change the code here that specifies how many times transient errors are generated. You could also change the code to generate more exceptions so that Entity Framework will throw the RetryLimitExceededException exception.
The value you enter in the Search box will be in command.Parameters[0] and command.Parameters[1] (one is used for the first name and one for the last name). When the value "Throw" is found, it is replaced in those parameters by "an" so that some students will be found and returned.
This is just a convenient way to test connection resiliency based on changing some input to the application UI. You can also write code that generates transient errors for all queries or updates, as explained later in the comments about the DbInterception.Add method.
-
In Global.asax, add the following Imports statements:
Imports ContosoUniversity.DAL Imports System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception
-
Add the highlighted line to the Application_Start method:
Sub Application_Start() AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas() FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters) RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes) BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles) DbInterception.Add(New SchoolInterceptorTransientErrors()) DbInterception.Add(New SchoolInterceptorLogging()) End Sub
These lines of code are what causes your interceptor code to be run when Entity Framework sends queries to the database. Notice that because you created separate interceptor classes for transient error simulation and logging, you can independently enable and disable them.
You can add interceptors using the DbInterception.Add method anywhere in your code; it doesn't have to be in the Application_Start method. Another option is to put this code in the DbConfiguration class that you created earlier to configure the execution policy.
Imports System.Data.Entity Imports System.Data.Entity.SqlServer Imports System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception Namespace DAL Public Class SchoolConfiguration Inherits DbConfiguration Public Sub New() SetExecutionStrategy("System.Data.SqlClient", Function() New SqlAzureExecutionStrategy()) DbInterception.Add(New SchoolInterceptorTransientErrors()) DbInterception.Add(New SchoolInterceptorLogging()) End Sub End Class End Namespace
Wherever you put this code, be careful not to execute DbInterception.Add for the same interceptor more than once, or you'll get additional interceptor instances. For example, if you add the logging interceptor twice, you'll see two logs for every SQL query.
Interceptors are executed in the order of registration (the order in which the DbInterception.Add method is called). The order might matter depending on what you're doing in the interceptor. For example, an interceptor might change the SQL command that it gets in the CommandText property. If it does change the SQL command, the next interceptor will get the changed SQL command, not the original SQL command.
You've written the transient error simulation code in a way that lets you cause transient errors by entering a different value in the UI. As an alternative, you could write the interceptor code to always generate the sequence of transient exceptions without checking for a particular parameter value. You could then add the interceptor only when you want to generate transient errors. If you do this, however, don't add the interceptor until after database initialization has completed. In other words, do at least one database operation such as a query on one of your entity sets before you start generating transient errors. The Entity Framework executes several queries during database initialization, and they aren't executed in a transaction, so errors during initialization could cause the context to get into an inconsistent state.
Test logging and connection resiliency
-
Press F5 to run the application in debug mode, and then click the Students tab.
-
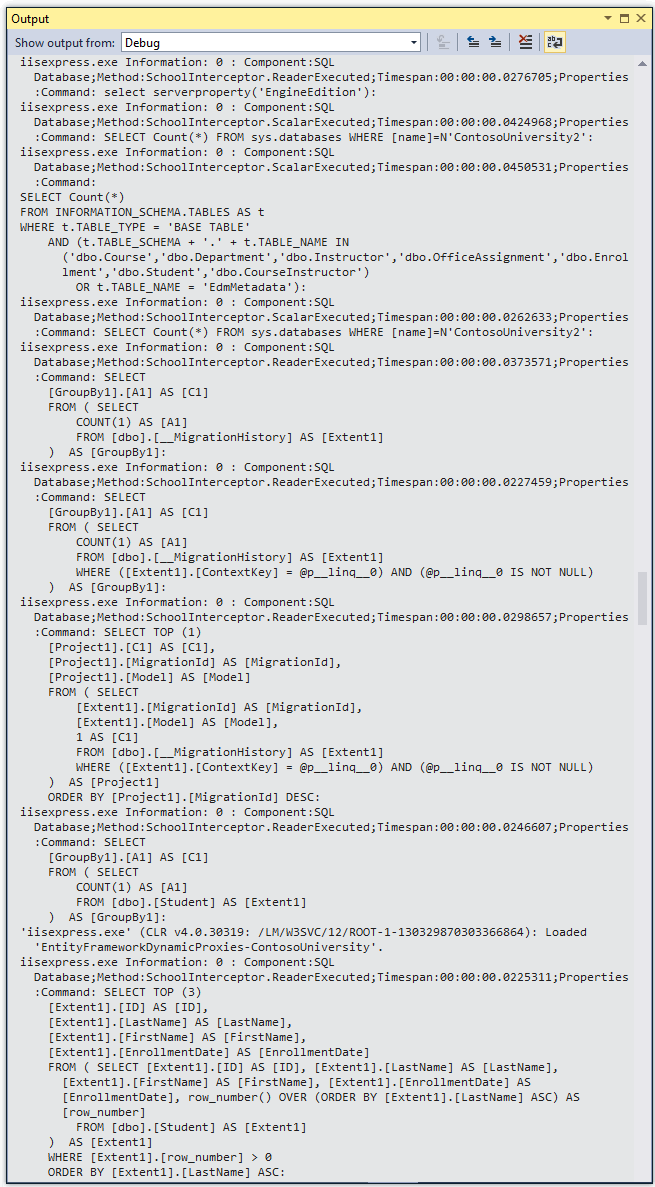
Look at the Visual Studio Output window to see the tracing output. You might have to scroll up past some JavaScript errors to get to the logs written by your logger.
Notice that you can see the actual SQL queries sent to the database. You see some initial queries and commands that Entity Framework does to get started, checking the database version and migration history table (you'll learn about migrations in the next tutorial). And you see a query for paging, to find out how many students there are, and finally you see the query that gets the student data.
- In the Students page, enter "Throw" as the search string, and click Search.
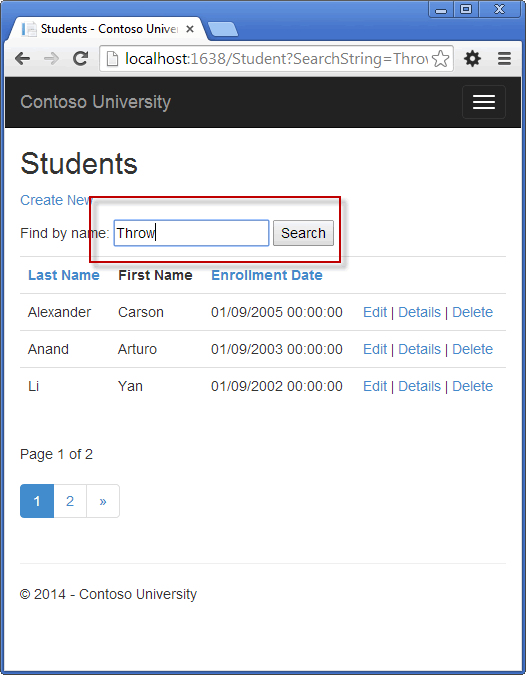
You'll notice that the browser seems to hang for several seconds while Entity Framework is retrying the query several times. The first retry happens very quickly, then the wait before increases before each additional retry. This process of waiting longer before each retry is called exponential backoff.
When the page displays, showing students who have "an" in their names, look at the output window, and you'll see that the same query was attempted five times, the first four times returning transient exceptions. For each transient error you'll see the log that you write when generating the transient error in the SchoolInterceptorTransientErrors class ("Returning transient error for command...") and you'll see the log written when SchoolInterceptorLogging gets the exception.

Since you entered a search string, the query that returns student data is parameterized:
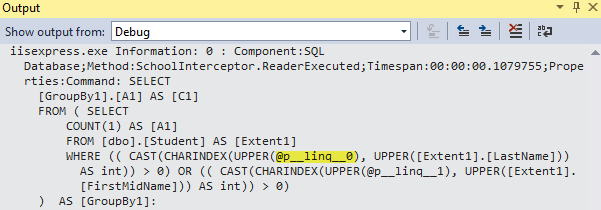
You're not logging the value of the parameters, but you could do that. If you want to see the parameter values, you can write logging code to get parameter values from the Parameters property of the DbCommand object that you get in the interceptor methods.
Note that you can't repeat this test unless you stop the application and restart it. If you wanted to be able to test connection resiliency multiple times in a single run of the application, you could write code to reset the error counter in SchoolInterceptorTransientErrors.
-
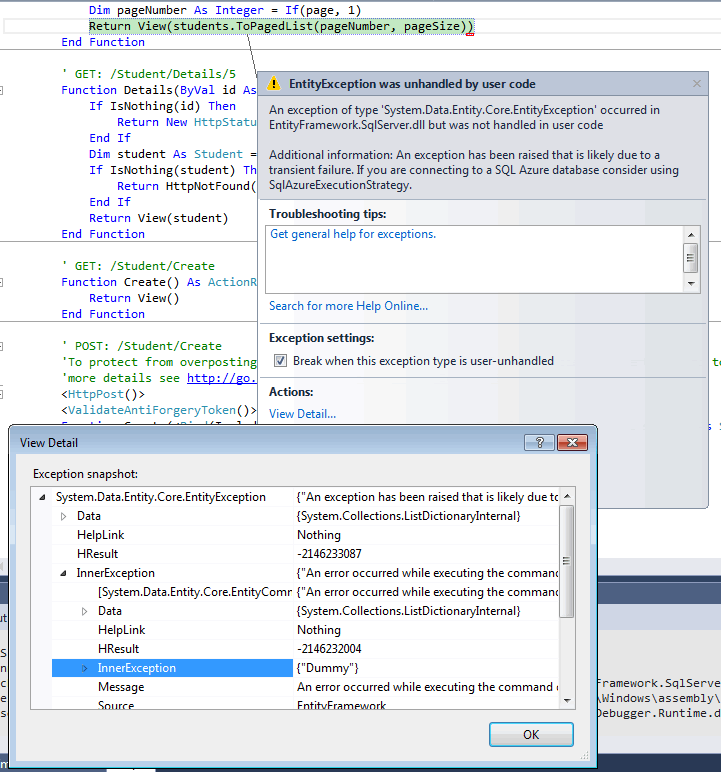
To see the difference the execution strategy (retry policy) makes, comment out the SetExecutionStrategy line in SchoolConfiguration.vb, run the Students page in debug mode again, and search for "Throw" again.
This time the debugger stops on the first generated exception immediately when it tries to execute the query the first time.
-
Uncomment the SetExecutionStrategy line in SchoolConfiguration.vb.
Summary
In this tutorial you've seen how to enable connection resiliency and log SQL commands that Entity Framework composes and sends to the database. In the next tutorial you'll deploy the application to the Internet, using Code First Migrations to deploy the database.
